If you’re preparing for the United States Medical Licensing Examination® (USMLE®) Step 1 exam, you might want to know which questions are most often missed by test-prep takers. Check out this example from Kaplan Medical, and read an expert explanation of the answer. Also check out all posts in this series.
This month’s stumper
A 72-year-old man with a history of diverticulitis is admitted to the intensive care unit with chills, fever, malaise, and confusion. He resides in a nursing home, and has been complaining of severe abdominal pain. His temperature is 40 °C (104 °F), his blood pressure is 84/58 mm Hg, his pulse is 111 beats per minute, and respirations are 22 per minute.
He remains hypotensive despite aggressive hydration. Physical examination shows rebound tenderness and guarding of his abdomen. A CT of the abdomen to shows pneumoperitoneum as well as bilateral adrenal hemorrhage. Laboratory studies show:
Sodium – 130 mEq/L
Potassium – 5.1 mEq/L
Glucose – 70 mg/dL
Which of the following laboratory findings is most likely present in this patient?
A. Elevated aldosterone.
B. Elevated cortisol.
C. Elevated renin activity.
D. Reduced adrenocorticotropic hormone.
E. Reduced corticotropin-releasing hormone.
The correct answer is C.
Kaplan Medical explains why
Lab findings indicative of low aldosterone must mean renin is elevated. This patient is suffering from septic shock. The pneumoperitoneum on CT indicates that bowel perforation occurred, from a ruptured diverticulum, for example.
Severe septic shock can lead to destruction of the adrenal cortex, which causes loss of mineralocorticoids as well as glucocorticoids (i.e., Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome). The adrenal gland receives a rich blood supply from the aorta and the inferior phrenic and renal arteries, which form a subcapsular plexus. Adrenal necrosis and hemorrhage may occur during hypotension and stress, resulting in vascular engorgement and stasis.
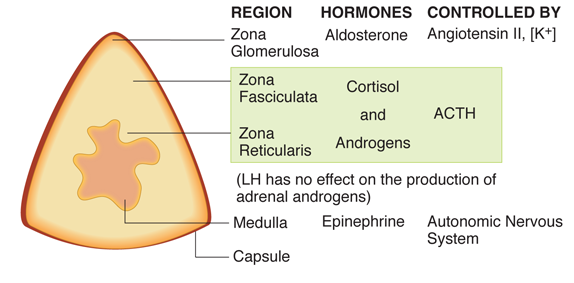
The mineralocorticoid deficiency (following injury to the zona glomerulosa; see figure) causes urinary loss of sodium and water, and retention of potassium. The hypotonic dehydration reduces renal perfusion; the compensatory response to this includes increased secretion of renin, which elevates renin activity.
Why the other answers are wrong
Choice A: The ischemic damage of the adrenal gland would cause decreased secretion of all adrenal steroids; thus aldosterone would not be increased.
Choice B: Damage to the zona fasciculata would result in decreased rather than an increased cortisol levels.
Choice D: Cortisol secretion is normally stimulated by the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary. Once cortisol is released, it feeds back to the pituitary to inhibit further ACTH secretion. Therefore, if cortisol secretion were impaired, ACTH levels would be elevated rather than reduced.
Choice E: Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is released by the hypothalamus and stimulates secretion of ACTH from the anterior pituitary. CRH release is subject to feedback inhibition by cortisol, so CRH levels would be increased in the absence of cortisol, not decreased.
Tips to remember
- Destruction of the adrenal cortex produces a mineralocorticoid deficiency, causing a hypotonic dehydration.
- This leads to reduced renal perfusion, producing a compensatory response that includes increased renin secretion and activity.
For more prep questions on USMLE Steps 1, 2 and 3, view other posts in this series.
The AMA and Kaplan have teamed up to support you in reaching your goal of passing the USMLE® or COMLEX-USA®. If you're looking for additional resources, Kaplan provides free access to tools for pre-clinical studies, including Kaplan’s Lecture Notes series, Integrated Vignettes, Shelf Prep and more.